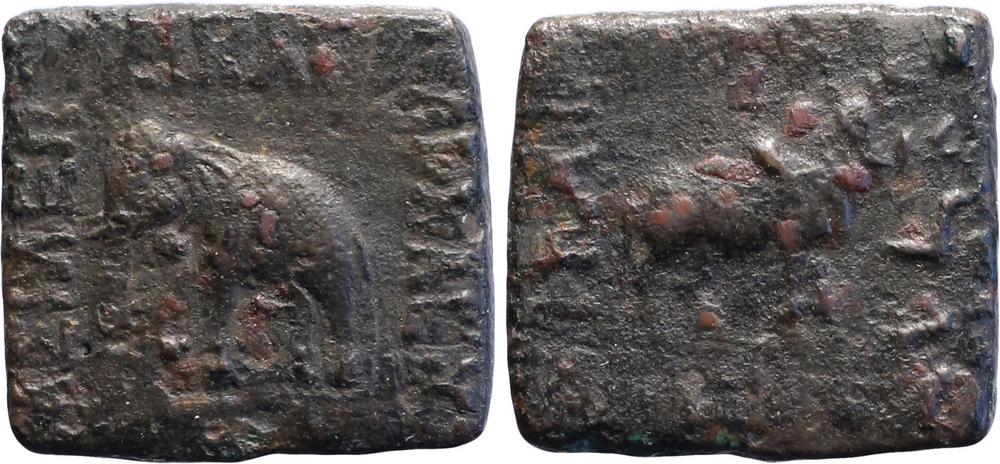
91 BCE - 75 BCEΒΑΣΙΛΕΩΣ ΔΙΚΑΙΟΥ ΗΛΙΟΚΛΕΟΥΣ | Maharajasa dhramikasa Heliyakreyasa (of Great king Heliokles the Just)
Overstruck variety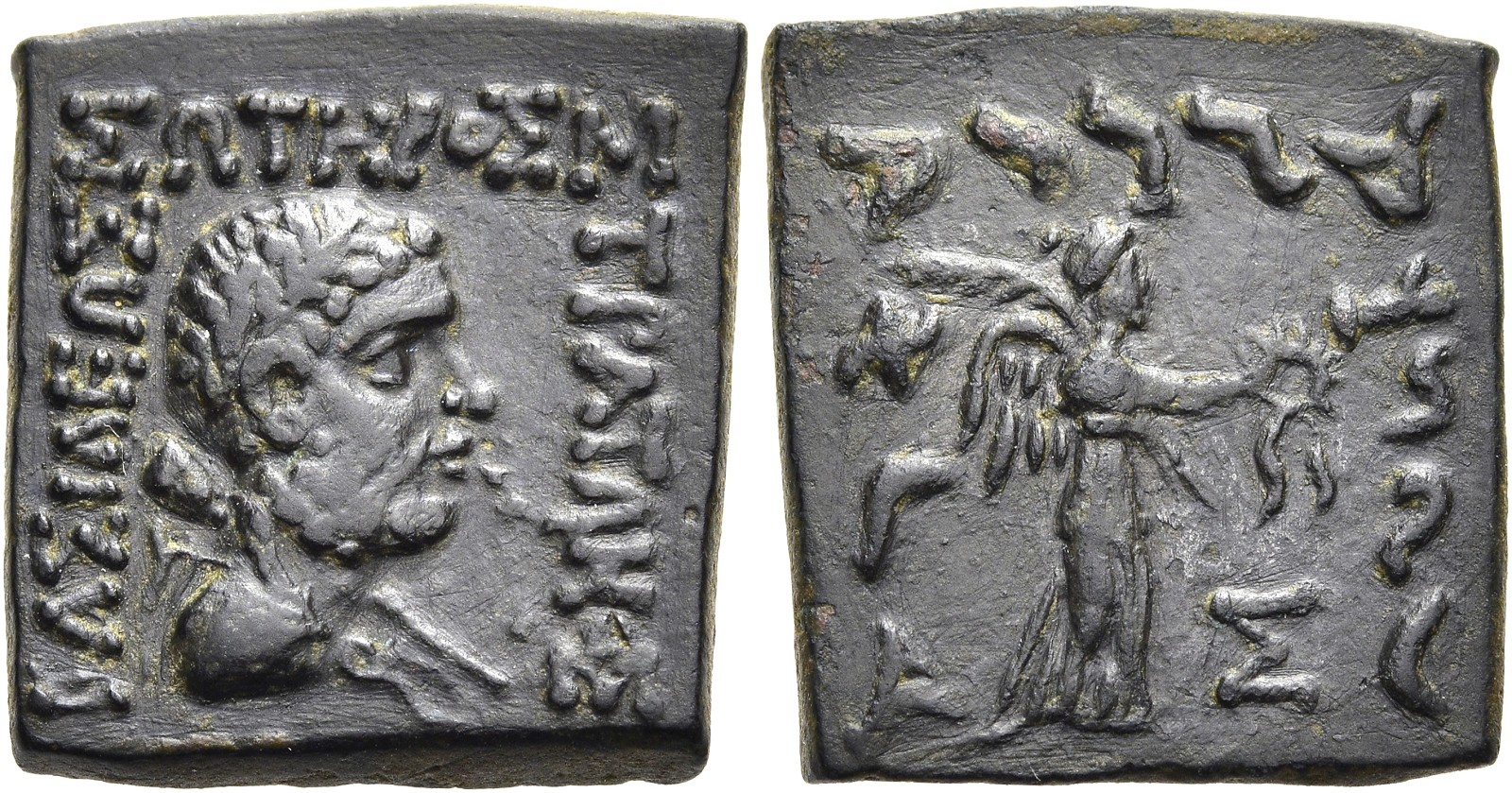
Strato_I_Heracles_Nike.jpeg
[2]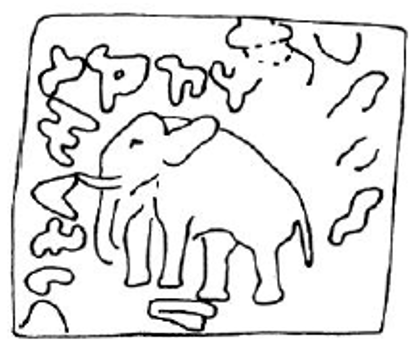
2085_Strato_I_overstruck_(drawing).png
Description
| ObverseInscription or printing placed on the obverse.:
|
ΒΑΣΙΛΕΩΣ ΔΙΚΑΙΟΥ ΗΛΙΟΚΛΕΟΥΣ (Greek) Elephant standing left.
|
ReverseInscription or printing placed on the reverse.:
|
Maharajasa dhramikasa Heliyakreyasa (of Great king Heliokles the Just) (Kharoshthi) Bull standing right. In exergue, monogram.
|
Mint and issuing power
Chronology
| FromIdentifies the initial date in a range assigned in a numismatic context. 91 BCE toIdentifies the final date in a range assigned in a numismatic context.. 75 BCE
|
hellenistic periodTime period of the numismatic object.
|
Physical description
MetalThe physical material (usually metal) from which an object is made.: Bronze 
|
WeightWeight of the numismatic object (in grams). in grams: 8.318.31 g <br />8,310 mg <br />
|
DenominationTerm indicating the value of a numismatic object. Examples: tetradrachm, chalkous, denarius.: denomination B
|
|
|
|
StandardStandard.: Indian (Hoover)
|
References
| Coin referenceReference of the Coin:
|
Bopearachchi 1989, p. 59, n° 8, pl. V
|
Coin series referenceReference to coin series study:
|
Mitchiner 19751Mitchiner 1975, p. 166, type 296., Bopearachchi 19912Bopearachchi 1991, p. 285 and pl. 42, série 8., HGC 123HGC 12, n° 385.
|
| Coin series web referenceCoin series web references:
|
|
Description
| ObverseInscription or printing placed on the obverse.:
|
ΒΑΣΙΛΕΩΣ ΣΩΤΗΡΟΣ ΣΤΡΑΤΟΝΟΣ (Greek) Bust of Heracles (nothing visible on obverse)
|
ReverseInscription or printing placed on the reverse.:
|
Mahajarassa tratarasa Stratasa (Kharoshthi) Nike walking right (visible on reverse: part of legend)
|
Mint and issuing power
Chronology
| FromIdentifies the initial date in a range assigned in a numismatic context. 110 BCE toIdentifies the final date in a range assigned in a numismatic context.. 85 BCE
|
Hellenistic 323-30 BC  periodTime period of the numismatic object. periodTime period of the numismatic object.
|
Physical description
| DenominationTerm indicating the value of a numismatic object. Examples: tetradrachm, chalkous, denarius. ᵖ:
|
denomination B
|
StandardStandard. ᵖ:
|
Indian module
|
References
References
- a b Mitchiner, Michael (1975), Indo-Greek and Indo-Scythian coinage, London,
- a b Bopearachchi, Osmund (1991), Monnaies gréco-bactriennes et indo-grecques : catalogue raissoné, Paris, 459 p., 69 pl.
- a b Hoover, Oliver D. (2013), Handbook of coins of Baktria and ancient India : including Sogdiana, Margiana, Areia, and the Indo-Greek, Indo-Skythian, and native Indian states south of the Hindu Kush, fifth century BC to first century, Lancaster-London,


